argon valence shell|Argon : Clark The number of electrons in the outermost shell of a particular atom determines its reactivity, or tendency to form chemical bonds with other atoms. This outermost shell is known as . NBA Spreads: Betting on the point spreads of NBA games. These NBA odds require a team to win or lose by a specific number of points, evening the playing field between unevenly matched teams. . Because there isn’t a point spread, the payout will change based on the moneyline odds. For the favorite, the odds to win is the dollar amount you .
PH0 · Valences of the Chemical Elements
PH1 · Valence electrons and ionic compounds (video)
PH2 · Valence electrons (video)
PH3 · Valence electron
PH4 · The periodic table, electron shells, and orbitals
PH5 · How many Valence Electrons are there in Argon?
PH6 · Electron Configuration for Argon (Ar)
PH7 · Argon Valence Electrons
PH8 · Argon
PH9 · 3.7: Electrons and Valence Shells
The Egg Company | 2,166 followers on LinkedIn. Digital marketing across Asia | There are over 2 billion internet users in Asia. . Digital Public Relations (PR), Content Marketing, Strategic Planning, Baidu SEO and PPC, Corporate Training, Media Buy China, Programmatic Buy China, Japanese Search Engine Optimization, Korean Search .
argon valence shell*******Group 18 elements (helium, neon, and argon are shown in Figure 2) have a full outer, or valence, shell. A full valence shell is the most stable electron configuration. .
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell, or energy level, of an atom. For example, oxygen has six valence electrons, two in the 2s subshell and four in the 2p .
You may assume the valences of the chemical elements—the number of .The number of electrons in the outermost shell of a particular atom determines its reactivity, or tendency to form chemical bonds with other atoms. This outermost shell is known as .The electrons that determine valence – how an atom reacts chemically – are those with the highest energy. For a main-group element, the valence electrons are defined as those electrons residing in the electronic shell of highest principal quantum number n. Thus, the number of valence electrons that it may have depends on the electron configuration in a simple way. For example, the electronic c.
It's not unreasonable for calcium to lose two electrons to have a stable outer shell, to have an electron configuration like argon. So if it loses two electrons it has a positive two . Argon is a noble gas with an electron configuration of #[Ne]3s^2\3p^6#. So, it has #3# electron shells, and that will be its valence shell. In the third shell, it holds a .This full valence shell makes argon very stable and extremely resistant to bonding with other elements. Before 1962, argon and the other noble gases were considered to be chemically inert and unable to form .
Well, Argon has an absolute zero valency. Argon holds 18 electrons in its outer shell with the electron configuration of 2,8,8. So, this is why Argon has no need to .Electron Configuration Notation: -shows the arrangment of electrons around the nucleus of an atom. - helps chemist understanding how elements form chemical bonds. - can be .The noble gases (Group 18) are located in the far right of the periodic table and were previously referred to as the "inert gases" due to the fact that their filled valence shells (octets) make them extremely . Valency of Argon. Well, Argon has an absolute zero valency. Argon holds 18 electrons in its outer shell with the electron configuration of 2,8,8. So, this is why Argon has no need to either gain or lose the electrons. The eight electrons fill the valence shell to bring about the 0 valencies of Argon. Check here for Argon Valence Electrons or .
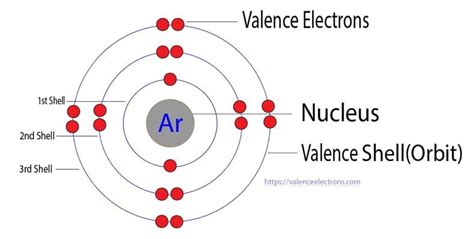
Electrons that are found in the outermost shell are generally known as valence electrons and the number of valence electrons determines the valency (or valence) of an atom. . Valency of Chlorine: 17: 1: .argon valence shell The atomic number of argon is 18. That is, the number of electrons in argon is eighteen. Therefore, the argon atom will have two electrons in the first shell, eight in the 2nd orbit, and eight electrons in the 3rd shell. Therefore, the order of the number of electrons in each shell of the argon(Ar) atom is 2, 8, 8.
These classifications determine which orbitals are counted in the valence shell, or highest energy level orbitals of an atom. Main group elements (sometimes called representative elements) are those in which the last electron added enters an s or a p orbital in the outermost shell, shown in blue and red in Figure 6.29. This category includes .
Element Argon (Ar), Group 18, Atomic Number 18, p-block, Mass 39.95. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images. . Members of a group typically have similar properties and electron configurations in their outer shell. Period A horizontal row in the periodic table. The atomic number of each element .Argon's complete octet of electrons indicates full s and p subshells. This full valence shell makes argon very stable and extremely resistant to bonding with other elements. Before 1962, argon and the other noble gases were considered to be chemically inert and unable to form compounds; however, compounds of the heavier noble gases have since .
Bohr diagrams indicate how many electrons fill each principal shell. Group 18 elements (helium, neon, and argon) have a full outer, or valence, shell. A full valence shell is the most stable electron configuration. Elements in other groups have partially filled valence shells and gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.Remember, valence electrons are the reactive electrons, the ones that might interact with other things. And because elements with similar valence electrons will have similar reactivities, they will form similar ions. . Neon's outer shell's the second shell, it's full. Argon's outer shell is the third shell and it's full, and so on and so . There are two ways to find the number of valence electrons in Argon (Ar). The first is to use the Periodic Table to figure out how many electrons Argon has i.Argon Contributors and Attributions. 3.10: Valence Electrons is shared under a CC BY-NC license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied principal energy level of an atom. In the second period elements, the two electrons in the 1s sublevel are called inner-shell electrons ..

Inner transition elements are metallic elements in which the last electron added occupies an f orbital. They are shown in green in Figure 3.4.6 3.4. 6. The valence shells of the inner transition elements consist of the ( n – 2) f, the ( n – 1) d, and the ns subshells. There are two inner transition series: This periodic table shows the valences of element groups. The transition metals make use of the d-subshell, which can accommodate 10 electrons.The f-subshell holds 14 electrons and the .argon valence shell Argon Explanation: Because of their full valence electron shell, the noble gases are extremely stable and do not readily lose or gain electrons. 7. Answer: S > Si > Al > Mg. Explanation: The electrons above a closed shell are shielded by the closed shell. S has 6 electrons above a closed shell, so each one feels the pull of 6 protons in the nucleus. 8. The shorthand electron configuration for Argon is [Ne] 3s 2 3p 6. The number of valence electrons available for the Argon atom is 8. Argon is situated in Group 18th or 8A and has an atomic number of 18. The first shell of Argon has 2 electrons and the outer shell or valence shell of Argon has 8 electrons, hence, the number of valence . Valence shell electrons (or, more simply, the valence electrons) are the electrons in the highest-numbered shell, or valence shell, while core electrons are the electrons in lower-numbered shells. We can see from the electron configuration of a carbon atom—1 s2 2 s2 2 p2 —that it has 4 valence electrons (2 s2 2 p2) and 2 core electrons . The electrons occupying the outermost shell orbital(s) (highest value of n) are called valence electrons, and those occupying the inner shell orbitals are called core electrons ( Figure \PageIndex5\PageIndex5). Since the core electron shells correspond to noble gas electron configurations, we can abbreviate electron configurations by writing . The valence electrons (i.e., the \(2s^22p^4\) part) are valence electrons, which do participate in the making and breaking of bonds. Similarly, in calcium (Equation \(\ref{3}\)), the electrons in the argon-like closed shell are the core electrons and the the two electrons in the 4s orbital are valence electrons.
Enhance your web development skills with our comprehensive tutorials on CSS3. Learn advanced styling properties, animations, and responsive design techniques to create visually appealing and interactive web pages.
argon valence shell|Argon